The spine consists of 5 sections, in each of which a degenerative process can occur, for example, osteochondrosis. This is a disease of the spinal column, accompanied by a change in the intervertebral disc. After a while, the intervertebral joints, the bodies of the adjacent vertebrae and the ligamentous apparatus begin to be involved in this process.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region occurs most often, because it is this department that experiences the maximum stress. Such a disease makes a person disabled and can even lead to disability.
How does pathology develop?
The structure of all vertebrae, except for the five coccygeal and the first two cervical, is practically the same: the body and the arch, which are connected to each other using arcuate bone beams. A hole is formed between them, which is called a vertebrate. Folding together, these holes form the spinal or vertebral canal, which contains the spinal cord.
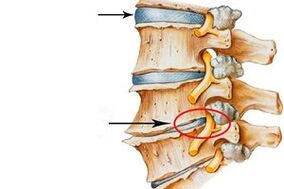
The processes of the vertebrae, extending from the arch in different directions, form various sedentary joints among themselves. In the holes that arise between those that go up or down, as well as to the sides, are the vessels and spinal nerves.
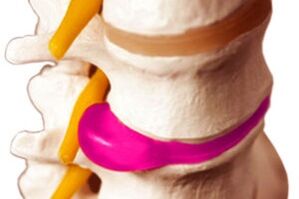
If osteochondrosis occurs, the initial changes affect the intervertebral disc. In a person after 30 years in such a disk, a deterioration of water exchange occurs, as a result of this, a degenerative process begins to develop, due to which its main fibrous part becomes brittle and thin. The nucleus pulposus, which is the jelly-like center of the intervertebral disc, begins to expand its boundaries, making a "move" towards the spinal canal.
This contributes to the compression of the spinal cord or nerves that branch out from it, edema occurs. As a result of this, pain occurs and the function of the organs to which the commands from these areas were received is disrupted.
Since the structure of the intervertebral disc undergoes changes, the sections located above it begin to exert increased pressure on the substance of the vertebra. This pressure promotes the accelerated division of bone cells, which leads to the formation of osteophytes. However, the intervertebral disc, which is cartilage, cannot be restored, and the dysfunction of organs from compression by osteophytes increases even more.
Causes of occurrence
There are several reasons leading to the occurrence of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. These include the following factors:
- Significant physical activity. If a person's professional activity is directly related to the movement of heavy objects, then he automatically falls into the risk zone.
- Overweight. Obesity puts stress on the spine and joints.
- Inactive lifestyle. If a person does not play sports, moves little or even does not do light exercises, then after a while he will have problems with the spine.
- Posture. If a person has the wrong sediment, and besides, he leads a sedentary lifestyle, then an incorrect distribution of the load on the spine occurs, due to which the lumbar region is subjected to increased stress, and he begins to suffer.
- Spine injury. Even if a minor injury is received, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine may occur after a while. Professional athletes are usually at risk.
- Additional factors. The following reasons contribute to the development of the disease - unhealthy diet, frequent stress, metabolic disorders, non-observance of the daily regimen.
- Features of the structure of the disks. Since the discs have a porous-loose structure, they are much more vulnerable to various deformations.
This disease affects not only the elderly, but also young people. Medical statistics indicate that quite often signs of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine are diagnosed in young people under 30 years of age. The disease affects both men and women.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptom of lumbar osteochondrosis is pain. At first, it occurs with excessive physical exertion, and disappears at rest. After a while, she begins to pester even with prolonged walking. The pain is constant, aching, and sometimes shooting. She can give it to the buttock, inner thighs, leg.
As soon as the distance between the vertebrae begins to decrease and the destruction of the intervertebral disc occurs, the following symptoms appear in the lumbar region - a feeling of heat or cold. Pain in the leg or back intensifies, "goose bumps" appear. With the progression of the disease, the spine turns around its axis with the formation of scoliosis and lordosis, and the nucleus pulposus is squeezed out to the side. In this case, the symptoms of osteochondrosis are manifested in the form of compression of the vessels and roots of the spinal nerves.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis manifest themselves in different ways and depends on which nerve root is squeezed between the vertebrae. The lower the degenerative process occurs, the closer to the feet the area will be located in which the following pathological conditions are noted:
- decreased tendon reflexes;
- reduction of pain and vibration sensitivity of tissues;
- tingling sensation, goose bumps.
Involvement in the process of bundles of nerve roots, which are a continuation of the spinal cord, is manifested by the following symptoms:
- intolerable back pain;
- loss of sensitivity on the inner thigh;
- constipation;
- decreased libido;
- pain or loss of sensitivity in the lower extremities;
- retention or urinary incontinence;
- violation of the menstrual cycle in women.
The last stage of lumbar osteochondrosis is accompanied by constant pain. Symptoms such as paralysis of the lower extremities, atrophy of the muscles of the legs can be observed. There is a violation of sexual function, as well as retention or incontinence of feces and urine.
Possible complications
A disease such as osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine can cause the following complications:
- intervertebral hernia;
- complete obstruction of the spinal canal;
- paralysis of the lower extremities;
- spinal cord compression;
- impotence;
- renal colic.
Diagnostics
When the first symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis appear, it is best to consult a doctor as soon as possible. According to the description of the patient's complaints, a vertebrologist or neurologist is able to make a preliminary diagnosis. In addition, during the examination, the doctor may detect the following characteristic signs of the disease:
- soreness when pressing certain points;
- asymmetry of the buttocks;
- hypo- and hyperlordosis, scoliosis;
- curvature of the Michaelis rhombus.
The following studies help to make a final diagnosis, as well as to determine the degree of progression of the disease and possible complications:
- computed tomography of the lumbar spine;
- X-ray examination;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment methods
Treatment of a disease such as osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is carried out in a comprehensive manner and includes a conservative and surgical technique.
Drug treatment
At the initial stage of the development of the disease, antiviral drugs are used, which must first be in the form of ointments. After a while, the treatment is continued with pills of pain relievers. The use of such drugs is prohibited in cases of gastritis or peptic ulcer disease.
Also, treatment for osteochondrosis is carried out with the help of muscle relaxants - drugs that help the muscles to relax, which allows the spine to align.
Treatment with chondoprotectors is carried out when there is still a cartilaginous layer between the vertebral bodies. These medicines allow you to restore the structure of the intervertebral disc, but only if they are taken for a long time - about 6 months.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis involves the use of a B vitamin.
Massage and manual therapy
These therapies are very effective in relaxing tense muscles and relieving pain and spasms. Thanks to manual therapy, the spine is given the necessary position. But only a specialist who should be guided by X-ray and tomographic images is obliged to carry out such procedures, and such treatment should be carried out in the subacute stage of the disease.
Physiotherapy treatment
With osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the following treatment is prescribed:
- UHF;
- amplipulse;
- magnetotherapy using a high frequency field.
Such procedures have an analgesic, vasodilatory, stimulating effect, and also improve blood flow in the affected area.
Other conservative treatments
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis will be ineffective without specific exercises. Only a doctor should select them, taking into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease. Additional methods of treatment are also prescribed: acupuncture, myostimulation, hirudotherapy, spinal traction. A good result is provided by treatment in a sanatorium, where patients undergo a full range of procedures in order to improve their health.
The duration of conservative therapy is 2-3 months. If, after the treatment, there were no improvements or, conversely, the disease began to progress, then the doctor usually recommends surgical treatment.
Surgery
Surgery is usually indicated in cases where there is a complication of the disease in the form of a hernia. The most common operation in this case is considered to be a disketomy, which consists in removing a damaged disk.
The most popular methods of surgical treatment are endoscopy and microsurgery. Their advantage lies in the fact that, unlike the classical methods, they are not so traumatic for the patient, they are completely bloodless and have a small risk of complications. When carrying out such operations, the muscles and ligaments are not damaged, since they are pushed apart with the help of special dilators of a small diameter, which look like a tube. The operation takes about one hour.
Prophylaxis
To avoid such a disease as osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the following rules must be observed:
- it is undesirable to be in a sitting position for a long time;
- with loads on the spine, a corset should be worn;
- during rest it is best to lie on your back;
- it is necessary to give up bad habits.
Thus, we examined the symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. This is a rather dangerous disease that, in its neglected state, makes a person disabled. Therefore, when the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is recommended to consult a doctor.